2000 Toyota Camry Timing Marks Pdf Free
Timing Chain Replacement Instructions
Timing belt at 60,000 miles. Avoid Costly Engine Damage. Change Your Timing Belt. At The Recommended Interval. Interference Engines & Timing Belt. 2.8L V6, 30-Valve *#. A4 Avant & Sedan. Turbo (AMB) *# T306. 105,000 Normal. 52,500 Severe. Statistical Techniques Statistical Mechanics.
The following are instructions on replacing the timing chain in a Toyota 22R/22RE/22RET without removing the head.
Parts needed:
- Timing Chain
- Chain Guides; metal backed are better than the stock plastic ones, two sources for these listed below:
- Chain Tensioner
- T-Chain Cover Gasket
- Water Pump Gasket
- Oil Pump O-ring
- Valve Cover Gasket
- Oil Pan Gasket or Toyota Black Form In Place Gasket (FIPG)
- Ultra Grey Silicone
- Can of Carb Cleaner
- 5 quarts of oil
- Gallon of Anti-freeze
- Toyota Red recommended plus a gallon of distilled water
The hardest step in the replacement will be breaking the bolt that holds the puley to the crankshaft. Best option is to break it loose with the engine's starter, tranny in neutral, wire off the coil. Use a 6-point (sided), 19mm, impact socket and a breaker bar long enough to reach the frame rail, then bump the starter until the bolt breaks free. Best to address this step early on in the process, instead of waiting until the engine is torn half-way down and starter operation is not possible. This is step 18 below. Other options include putting the tranny in 5th gear, engage 4WD if possible, e-brake on, chock the wheels and see if the clutch will hold the engine from turning; or pull the starter and try to jam a pry bar into the flywheel teeth to lock it in place. It is a good idea to place the engine at TDC prior to removing the crank pulley from the engine.
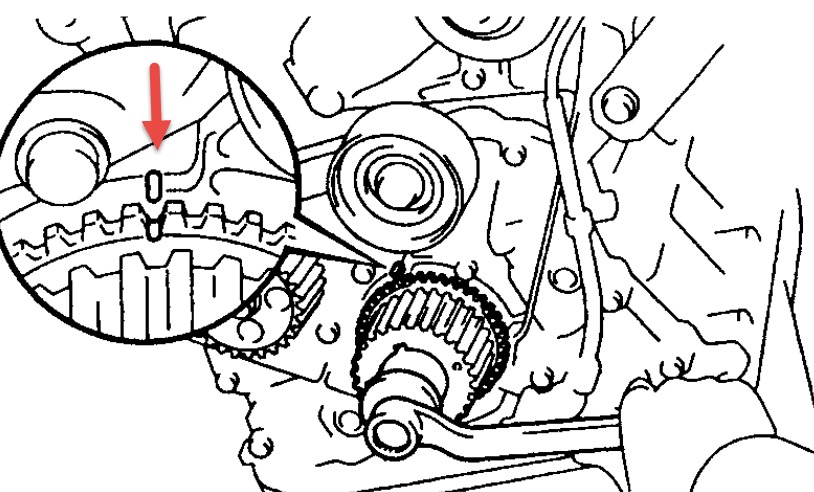
2000 Toyota Camry Timing Marks Pdf Free Download
- Be sure to get all of the old gasket off and wipe down the mating surfaces with carb cleaner to remove the oil residue so the new silicone sticks.
- If you just removed the two front bolts put them back in.
| Power Steering Bracket | P/S and alternator detail |
- 51. Put the coolant hose back on the tubes below the power steering pump.
- Be sure all the hose clamps are oriented to clear the brackets and to allow future removal if the need arises.
- 52. Put the alternator back on the mounts.
- 53. Put the distributor back in and take a guess at the timing.
- Helpful to have scribed a mark where it was before you removed it.
- 54. Put the pulley back on the crank and torque it to 130lbs.
- 55. Put the belts back on the vehicle and adjust them properly.
- 56. Put the radiator back in the vehicle and connect the hoses.
- 57. Fill the vehicle with 60% coolant 40% water.
- The best way to do this is a gallon of coolant than fill the container with water and keep adding it as the radiator drops.
- Filling the cooling system can take a while so just be patient.
- It also helps to have the vehicle parked on a slight uphill slope so the radiator is the highest point in the cooling system.
- 58. Fill the vehicle with oil.
- 59. Install distributor
- Install with engine at TDC for a 22R or 5° BTDC for a 22RE/REC/RET
- Set the distributor at the 12 o-clock position
- Upon insertion, it'll turn ~35° CCW and the timing will be close
- 60. Start up the vehicle.
- The timing is probably off since the distributor was moved.
- To get the vehicle to idle smoothly adjust the distributor freehand or set the timing the right way.
- With the timing test connector (TE+ E+) shorted, set the timing to 5° BTDC on the 22RE engine
- With the vacuum line disconnected from the distributor, 0°BTDC on the 22R engine
- Be sure and watch for good oil pressure and change your oil and filter after about 2000 miles
- And warm the engine up with the radiator cap off and the heater control to full heat until the thermostat opens.
- This will ensure any air pockets are flushed out of the cooling system.
- Top off the coolant as needed before installing the radiator cap.
- Author: Tim Macy
- Edited: Roger Brown
- If you would like to use this document or any of its contents for any publication, ask permission first.
Visitor #501048 since 18.MAY.2002
[Last updated: 12.January.2017]
VVT-i, or Variable Valve Timing with intelligence, is an automobilevariable valve timing technology developed by Toyota. The Toyota VVT-i system replaces the Toyota VVT offered starting in 1991 on the 5-valve per cylinder 4A-GE engine. The VVT system is a 2-stage hydraulically controlled cam phasing system.
VVT-i, introduced on the 1JZ-GTE/2JZ-GTE engine in 1996, varies the timing of the intakevalves by adjusting the relationship between the camshaft drive (belt or chain) and intake camshaft. Engine oil pressure is applied to an actuator to adjust the camshaft position. Adjustments in the overlap time between the exhaust valve closing and intake valve opening result in improved engine efficiency.[1] Variants of the system, including VVTL-i, Dual VVT-i, VVT-iE, VVT-iW and Valvematic, have followed.
VVTL-i[edit]
VVTL-i (Variable Valve Timing and Lift intelligent system) (also sometimes denoted as VVT-iL or Variable Valve Timing and Intelligence with Lift) is an enhanced version of VVT-i that can alter valve lift (and duration) as well as valve timing. In the case of the 16 valve 2ZZ-GE, the engine head resembles a typical DOHC design, featuring separate cams for intake and exhaust and featuring two intake and two exhaust valves (four total) per cylinder. Unlike a conventional design, each camshaft has two lobes per cylinder, one optimized for lower rpm operation and one optimized for high rpm operation, with higher lift and longer duration. Each valve pair is controlled by one rocker arm, which is operated by the camshaft. Each rocker arm has a slipper follower mounted to the rocker arm with a spring, allowing the slipper-follower to freely move up and down with the high lobe without affecting the rocker arm. When the engine is operating below 6000-7000 rpm (dependent on year, car, and ECU installed), the lower lobe is operating the rocker arm and thus the valves, and the slipper-follower is freewheeling next to the rocker arm. When the engine is operating above the lift engagement point, the ECU activates an oil pressure switch which pushes a sliding pin under the slipper-follower on each rocker arm. The rocker arm is now locked into the slipper-follower's movements and thus follows the movement of the high rpm cam lobe and will operate with the high rpm cam profile until the pin is disengaged by the ECU. The lift system is similar in principle to HondaVTEC operation.
The system was first used in 1999 Toyota Celica with 2ZZ-GE. Toyota has now ceased production of its VVTL-i engines for most markets, because the engine does not meet Euro IV specifications for emissions. As a result, this engine has been discontinued on some Toyota models, including that of the Corolla T-Sport (Europe), Corolla Sportivo (Australia), Celica, Corolla XRS, Toyota Matrix XRS, and the Pontiac Vibe GT, all of which had the 2ZZ-GE engine fitted. The Lotus Elise continues to offer the 2ZZ-GE and the 1ZZ-FE engine, while the Exige offers the engine with a supercharger.
Dual VVT-i[edit]
The Dual VVT-i system adjusts timing on both intake and exhaust camshafts. It was first introduced in 1998 on the RS200 Altezza's3S-GE engine.
Dual VVT-i is also found in Toyota's new generation V6 engine, the 3.5-litre 2GR-FE first appearing on the 2005 Avalon. This engine can now be found on numerous Toyota and Lexus models. By adjusting the valve timing, engine start and stop occurs almost unnoticeably at minimum compression. Fast heating of the catalytic converter to its light-off temperature is possible, thereby reducing hydrocarbon emissions considerably.
Most Toyota engines including the LR engines (V10, used in the Lexus LFA), UR engines (V8), GR engines (V6), AR engines (large I4), ZR engines (medium I4), and NR engines (small I4) now use this technology.
VVT-iE[edit]
VVT-iE (Variable Valve Timing - intelligent by Electric motor) is a version of Dual VVT-i that uses an electrically operated actuator to adjust and maintain intake camshaft timing.[2] The exhaust camshaft timing is still controlled using a hydraulic actuator. This form of variable valve timing technology was developed initially for Lexus vehicles. This system was first introduced on the 2007MY Lexus LS 460 as 1UR engine.
The electric motor in the actuator spins together with the intake camshaft as the engine runs. To maintain camshaft timing, the actuator motor will operate at the same speed as the camshaft. To advance the camshaft timing, the actuator motor will rotate slightly faster than the camshaft speed. To retard camshaft timing, the actuator motor will rotate slightly slower than camshaft speed. The speed difference between the actuator motor and camshaft timing is used to operate a mechanism that varies the camshaft timing. The benefit of the electric actuation is enhanced response and accuracy at low engine speeds and at lower temperatures as well as a greater total range of adjustment. The combination of these factors allows more precise control, resulting in an improvement of both fuel economy, engine output and emissions performance.
VVT-iW[edit]
VVT-iW (Variable Valve Timing - intelligent Wide) was introduced with the 2.0L turbochargeddirect-injected8AR-FTS fitted to the Lexus NX200t. VVT-iW uses VVT-iW on the intake valves and VVT-i on the exhaust valves. The intake cam has mid-position cam lock mechanism that retards the continuously variable timing. It offers expanded valve opening angles (Wide) which enables the engine to operate in a modified-Atkinson cycle at low rpm for improved economy and lower emissions, and in the Otto cycle at high rpm for better performance, while delivering high torque throughout the rpm band.[3]
Valvematic[edit]
The Valvematic system offers continuous adjustment to valve lift and timing and improves fuel efficiency by controlling the fuel/air intake using valve control rather than conventional throttle plate control.[4] The technology made its first appearance in 2007 in the Noah[5] and later in early-2009 in the ZR engine family used on the Avensis. This system is simpler in design compared to Valvetronic and VVEL, allowing the cylinder head to remain at the same height.
VVT-i Oil Supply Hose Issues[edit]
In 2010, Toyota USA announced a Limited Service Campaign (LSC 90K) to replace the rubber portion of the oil supply hose for the VVT-i actuator on the 2GR-FE (V6) engine, which were found to be defective. In all, approximately 1.6 million vehicles manufactured prior to 2008 were affected. The defective oil supply hoses were prone to degradation and eventual rupture, causing oil to rapidly leak and resulting in permanent engine damage.
In 2014, the LSC 90K Campaign was extended to 31 December 2021[6] on 117,500 Toyota brand vehicles that were 'missed' during the initial campaign.
See also[edit]
- Gasoline Direct Injection (Toyota D4 and D4-S)
References[edit]
- ^'Variable Valve Timing Mechanism on Toyota'. YouTube. 2006-09-10. Retrieved 2009-06-29.
- ^'Lexus LS engine page'. Archived from the original on 2009-05-03. Retrieved 2009-09-29.
- ^'Camry in Europe features new 2.0L engine with VVT-iW.' Green Car Congress. 2014-09-05. Retrieved 2016-06-27.
- ^'Toyota Develops Next-generation Engine Valve Mechanism — 'Valvematic' Achieves High Fuel Efficiency and Dynamic Performance —'. TOYOTA. 2010-06-12. Retrieved 2009-06-29.
- ^Nunez, Alex (2011-07-01). 'Toyota Noah / Voxy: Valvematic for the people (movers)'. Autoblog.com. Retrieved 2009-06-29.
- ^'Extension of Limited Service Campaign (LSC) 90K'(PDF). US: Toyota. Retrieved 2016-10-08.
External links[edit]
- Video animation of VVT-i can be found here (courtesy of PT. Toyota-Astra Motor, Indonesia)